[trigonometric function]
Juliaで描画.
import Pkg; Pkg.add("Plots")
using Plots
f(x) = cos(x)
x=0.0:0.2:2.5π #x=0からx=2πまで,0.2刻みの配列を生成
y=f.(x) #関数fをxに適用
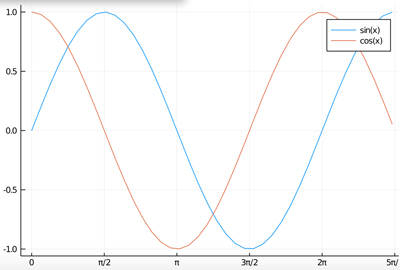
f2(x) = sin(x)
x=0.0:0.2:2.5π
y2=f2.(x) #関数f2をxに適用
xticks_values = [0,π/2,π,3π/2,2π,5π/2]
xticks_labels = ["0","π/2","π","3π/2","2π","5π/2"]
yticks_values = [-1.0,-0.5,0,0.5,1.0]
yticks_labels = ["-1.0","-0.5","0.0","0.5","1.0"]
plot(x,y2,labels="sin(x)",xticks = (xticks_values,xticks_labels),
yticks = (yticks_values,yticks_labels),
)
plot!(x,y,labels="cos(x)",xticks = (xticks_values,xticks_labels),
yticks = (yticks_values,yticks_labels),
)
Pythonで描画.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy import *
import pylab as plt
#“linspace(開始値,終了値,分割数)”で線形数列を生成
x = linspace(-3*pi, 3*pi, 150)
#数列をsinの引数に入れて,sin(x)の数列を生成
y = sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y, color="k", marker="o",markersize="2")
#plotした関数を表示
plt.show()

$\angle \theta$ の余角(co-angle)は $90^\circ - \angle \theta$ となります.
そうすると,余弦,余割,余接は余角に対する正弦,正割,正接として表されます.\[cos \theta = sin(90^\circ - \theta)\]\[cosec \theta = sec(90^\circ - \theta)\]\[cot \theta = tan(90^\circ - \theta)\]

ここで,\[sin \theta = \frac{b}{a}\]なので,\[a \cdot sin \theta = b\tag{1}\]となる. また,\[cos \theta = \frac{c}{a}\]なので,\[a \cdot cos \theta = c\tag{2}\]となる. $(1)$と$(2)$から,\[\begin{align} a^{2} &= b^{2}+c^{2} \\ &=a^{2} \cdot sin^{2} \theta + a^{2} \cdot cos^{2} \theta\\ &=a^{2}\cdot (sin^{2} \theta + cos^{2} \theta ) \end{align} \]両辺を $a^{2}$ で割ると,以下の関係式が得られる. 【公式】ピタゴラスの基本三角関数公式 この関係式は,ピタゴラスの基本三角関数公式[Fundamental Pythagorean trigonometric identity]と言われる. ピタゴラスの定理[Pythagorean theorem]は直角三角形に対して成り立つ定理である.これを直角三角形以外に一般化したものが第2余弦定理[law of cosines, cosine formula]である.なお,一般的に余弦定理と言えば,第2余弦定理のことを指す. 上の図から,\[cos \theta =\frac{d}{a}\]となるので,\[d=a \cdot cos \theta\]となる. さらに,\[sin \theta = \frac{e}{a}\]なので,\[e = a \cdot sin \theta\]となる. ここで,\[\begin{align} f &= c-d \\ &=c-a \cdot cos \theta \end{align} \]であることより,\[b^{2}=e^{2}+f^{2}\]というピタゴラスの定理に,\[e=a \cdot sin \theta\]\[f=c-a \cdot cos \theta \]を代入し,\[\begin{align} b^{2} &=e^{2}+f^{2} \\ &=(a \cdot sin \theta)^{2}+(c-a \cdot cos \theta)^{2}\\ &=a^{2} \cdot sin^{2}\theta + c^{2}-2ac \cdot cos \theta + a^{2} \cdot cos^{2} \theta \\ &=c^{2}+a^{2}(sin^{2}\theta+cos^{2}\theta)-2ac \cdot cos \theta \end{align}\]ここで,ピタゴラスの基本三角関数公式より,\[sin^{2}\theta+cos^{2}\theta=1\]であるから,結局,以下の定理が成り立つ. 【定理】第2余弦定理
ピタゴラスの定理の一般化と第2余弦定理
